Back pain is a common problem among middle -aged and elderly patients. It can be caused by a wrong lifestyle, pathology of the musculoskeletal system, diseases of internal organs. Neurologists, orthopedists, nephrologists and urologists can treat back pain, depending on its origin. It is difficult for the patient to know the cause of the unpleasant sensation itself and choose the right doctor. Therefore, initially it is necessary to contact a therapist, who, depending on the symptoms, history and results of the study conducted, will refer you to a narrow specialist.
Welding
Back pain can be:
- Myofascial.
- Nociceptive.
- Neuropathy.
- Psychogenic.
Myofascial painobserved during the formation of what is called. trigger point on the back muscles. The trigger point is a nut -like knot that forms when muscles are constantly tense (when they cannot relax). Moreover, when one segment of a muscle fiber is compressed, the other is stretched. This affects the movement of muscle fibers: it is limited. The fiber itself is shortened, becoming tighter.
The trigger point arises from muscle tension. Moreover, overtrain can occur not only due to excessive physical activity, but also due to prolonged in one position (e. g. , sitting at a computer). Trigger points also often occur with osteochondrosis.
Another factor that contributes to the formation of trigger points is excessive sarcoma stimulation (the basic contractile unit that is a protein complex). If there is excessive stimulation of the sarcoma, they are always in a contracted state.
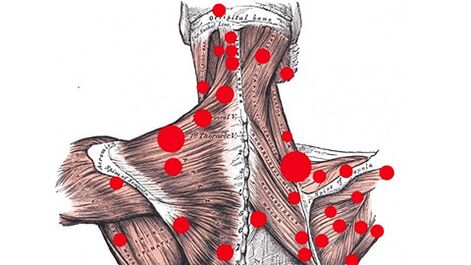
The presence of a trigger point does not allow the muscle to relax completely. He started to get tired quickly even with a small load, did too much movement while moving and recovered very slowly. Its limited range of motion affects the entire facial chain. Other muscles as well as some joints also become less mobile.
Blood flow in the tissues around the trigger point also suffers. Therefore, oxygen starvation is observed in this area. Decay products accumulate, irritate the trigger point, and pain develops because of this. In this case, muscle size is not a problem, it all depends on the degree of irritation of the point. Even the smallest muscle with a trigger point in it can give a lot of unpleasant sensations.
A characteristic feature of myofascial pain is their reflection. This means that the pain is reflected to other parts of the body. They can occur in areas very far from the trigger point. So, for example, pain under the shoulder blades or in the lower back can develop due to the presence of varicose veins in the abdominal muscles. Also, the lower back can be sore because of trigger points in the calf area or in the buttocks.
Myofascial pain is usually long lasting and dull. Sometimes it happens only while moving, sometimes at rest. Its strengths vary: from minor discomfort to unbearable pain.
Nociceptive pain- the body's response to direct irritation of pain receptors (nociceptors). For the posterior part, these are receptors located in the paravertebral ligaments, muscles, tendons, and also on the articular capsule of the intervertebral joint and the outer third of the fibrous ring of the intervertebral disc. Patients may experience pain with reflex muscle spasms, dystrophic or pathological processes in the facet joints. While moving, the pain gets stronger.
Neuropathic paindevelop in pathological processes in the nervous system: damage to the nerves or roots of the peripheral nervous system, disorders of the central nervous system. Such pain can be observed with osteoporosis, spondylolisthesis, hernias, and vertebral fractures. They get stronger when bending, moving, straining, coughing, sneezing, and in most cases they are given to the limbs. Sometimes they are dull and painful, but more often sharp shots.
Psychogenic painoccurs due to muscle spasms caused by emotional stress, chronic stress, or anxiety disorders.
In some cases, the varieties can be combined with each other. For example, myofascial sensations coexist with noseptive sensations.
Back pain is divided into 3 types:
- Acute (lasts less than 6 weeks).
- Subacute (6-12 weeks).
- Chronic (more than 3 months).
Acute / subacute painusually develops due to tissue damage (deep, superficial) as a result of cuts, wounds, inflammation. Therefore, the body warns us that something is wrong. The pain disappears after the tissue is completely healed.
Chronic painoccurs due to diseases of organs and systems or emotional disorders. If any, a thorough medical examination is required.
Depending on the location, the pain can be:
- Local.
- Mirrored.
- Shining.
Local pain develops directly at the site of development of pathological processes. Mirrored - if there is a trigger point. Radiation - with damage to internal organs, spreading along nerve fibers.
Why does my back hurt?
Back pain can be caused by a variety of reasons, including:
- Curvature of the spine: scoliosis, kyphosis.
- Neurological diseases: herniated intervertebral disc, osteochondrosis, spondylosis, spondyloarthrosis.
- Endocrine pathology: osteoporosis.
- Diseases of the respiratory system: pleurisy.
- Pathology of the kidneys and urinary system: urolithiasis, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis.
- Growth.
Short -term pain (usually severe, burning) can be caused by a variety of reasons. This includes:
- Injuries.
- Excess muscle (due to monotonous posture or performance of similar repetitive movements).
- Hypothermia.
Pain caused by degenerative processes occurs with the following diseases:
- Osteochondrosis.
- Intervertebral hernia.
- Protrusion of the intervertebral disc.
- Spondylosis deformans.
- Degenerative scoliosis.
- Arthrosis.
- Spondylolisthesis (displacement of the vertebrae).
- Spondylolysis (non -consolidation of the vertebral arch).
- Spinal stenosis.
Pain that radiates to the spine can arise due to disease:
- Heart and large ducts: myocardial infarction, angina pectoris, aortic aneurysm.
- Lungs: cancerous tumors, pleurisy.
- Esophagus.
- Gallbladder and bile ducts: acute and chronic cholecystitis.
- Kidneys and urinary tract.
- Pancreas.
Back pain in rare cases can be contagious. For example, sometimes my back hurts from the flu. Infections can also enter the spine from nearby organs: urinary tract, kidneys.
Another reason for the development of back pain may be changes in hormone levels (for example, related to age, during or after menopause). In this case, hormonal spondylopathy occurs (degenerative changes in the spine)
Back hurts a lot: what to do?
If you are having a severe pain attack, make sure you see a doctor as soon as possible. However, if the sensation is so strong that any movement causes torture, first aid is needed. You need to lie on your back on a flat, hard surface (for example, the floor). This will help relieve cramps, relax muscles, and reduce pain.
Sink on a flat surface, do not change the position of your back. Lying on your back, try to roll to your side. This will relieve the spine. When the pain subsides, turn around. It is recommended to put something under your feet, lifting it. Lie in this position for 10-15 minutes.
You also need to climb properly: first roll over on your side. From this position, get all four. Then lean on something (if there is no support nearby - crawl there) and slowly get up. Just by straight straightening your back.
To find out why your back hurts so badly, don’t delay a visit to the doctor. This will help prevent new attacks.
Diagnostics
You must make an appointment with a therapist if back pain:
- appear during physical exercise, muscle tension;
- lasts more than 3 days;
- repeated episodes.
You should immediately see a doctor in the following cases:
- back pain constantly;
- increased body temperature, numbness of the limbs, fatigue of the limbs in the morning coupled with pain;
- in the supine position, the pain does not disappear;
- severe pain at night.
During the appointment, the doctor will collect anamnesis, examine the patient (assess skin condition, body position and symmetry, gait, etc. ). Then he will give a study:
- general analysis of blood and urine;
- X-ray;
- computed tomography;
- magnetic resonance imaging.
If necessary, the therapist will refer the patient to a neurologist, orthopedist, urologist, gynecologist or nephrologist.
Treatment of back pain
Back pain treatment is comprehensive and may include:
- taking medications (anti-inflammatory, painkillers, restorative medications);
- restriction (long -term pain relief);
- physiotherapy procedures;
- physiotherapy training;
- massage;
- manual therapy.
If conservative methods do not give the desired result, surgical treatment is prescribed. Modern methods make it possible to perform accurate low -trauma surgery with a short recovery period.
Prevention of back pain
Simple preventative measures can help prevent back pain. It needs to:
- Monitor your body posture.
- Sleep on a bed with a hard mattress.
- Engaged in activities involving long sitting positions (driving, working at the computer), need to change posture from time to time, as well as arrange rest and warm -up.
- When standing for a long time, lean on something.
- Do not wear high heels for more than 2 hours in a row.
- Spend time with moderate physical activity (swimming, fitness).
- Keep track of your weight - back pain can occur due to the presence of extra pounds.
- Try not to lift weights.
- Do not twist or bend with sudden movements.
- Treat urological and gynecological diseases in a timely manner.
Annual preventive visits to a therapist will also be beneficial. Pathologies identified at an early stage can be eliminated without waiting for the development of complications.






















